Knowledge Base
What is MAG DRIVE PUMP?
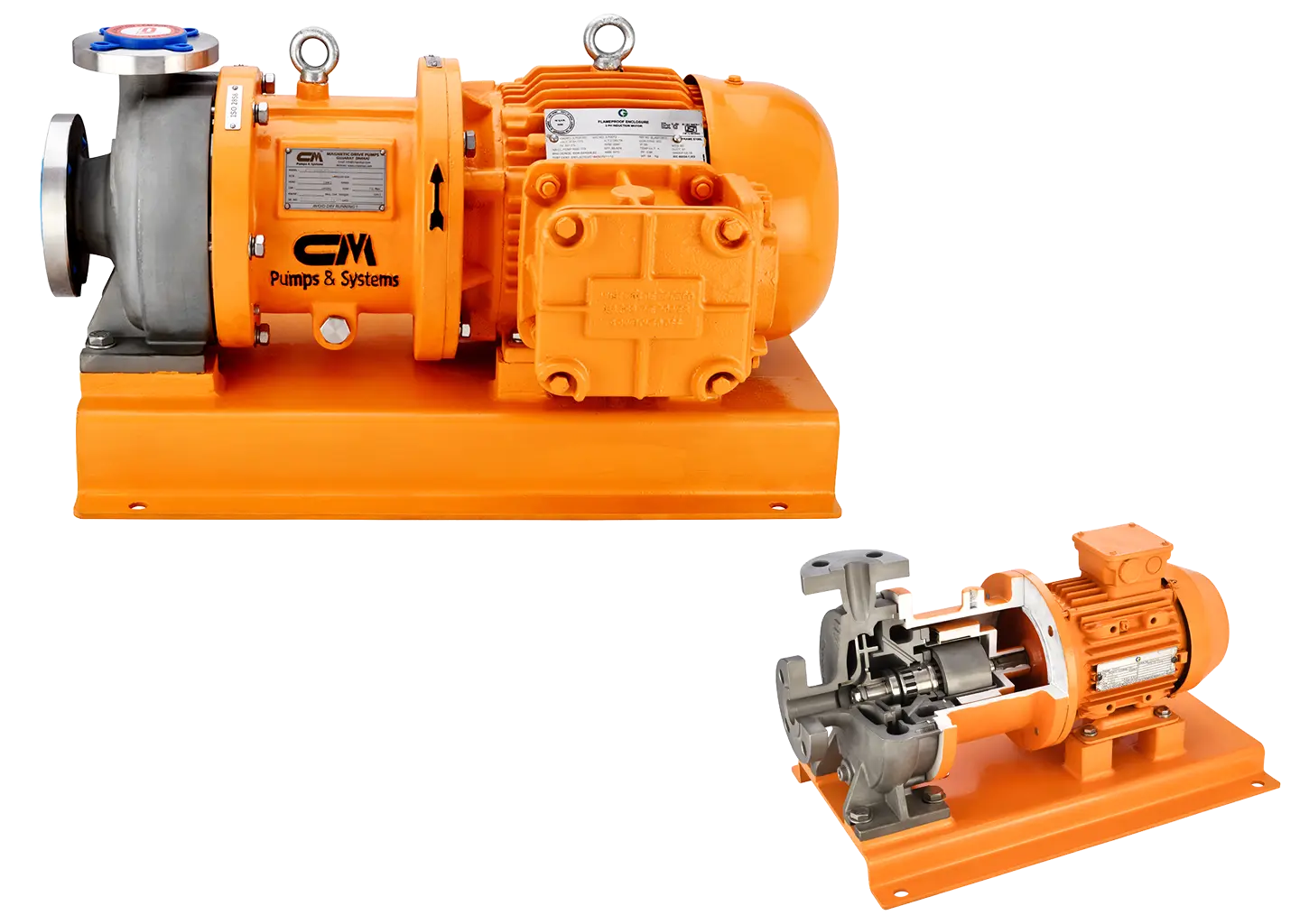
Magnetic drive pumps are typically used where leakage of the pumped liquid poses a great risk such as with aggressive or risky liquids, exotic materials, acids, alkalis, corrosives, pollutants and toxics. They are also used for ultra-pure liquids and hard-to-seal liquids. Sealed pumps applied to these types of services may leak over time or require complex, expensive double seals to prevent hazardous/challenging liquids from escaping to the atmosphere, which can lead to safety hazards, downtime and increased maintenance requirements.
Another important application for magnetic drive pumps is for difficult liquids; for example, some liquids can crystallize on seal faces, which then can cause seal failures. To avoid this, a permanent flush system should be run to the seal. This, however, can increase the cost of maintenance, seal flushing liquids and energy consumption. A better solution for these difficult services is to use a magnetic drive pump.
Mag-drive pumps are available in close-coupled and long-coupled (frame mounted) configurations.
Magnetic drive pumps have no direct connection between the electric motor shaft and the impeller; therefore, no seal is needed. There is no risk of leakage unless the pump casing is broken. Seals are known as a major cause of pump trips and unscheduled shutdowns. Obviously, the elimination of seals is a great improvement for performance, reliability and availability of pumps. The risk of leakage is completely eliminated; this means that liquids can be pumped without spillages. Eliminating the seals also gets rid of associated friction loss, wear, costs and noise. This provides complete separation of liquid from the pump drive and better transfer of motor power to the pump. There is practically no heat transfer from the electric motor because the pump chamber is completely separated from the electric motor by a large air gap; this provides an effective barrier between the two. The magnetic coupling will soften any shock or spike torques. Even in extreme situations, it will act as a fuse. Magnetic couplings can be broken temporarily if the load of the pump is too great. In practice, it means the pump does not overload and get damaged.
Magnetic drive pumps are available in most metallurgies and materials, metallic and non-metallic. Polymer lining pumps are also used because they offer improved corrosion resistance. Polymer coating options include polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), perfluoroalkoxy alkanes (PFA) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). These lined or non-metallic options are usually employed for ordinary temperatures, below 90°C as a rough indication. Metallic magnetic drive pumps have been used for even higher temperatures.
