Knowledge Base
- Home
- /
- Knowledge Base
- /
- Why are magnetic drive...
Why are magnetic drive pumps used?
A pump seal requires monitoring and frequent maintenance to avoid excessive leakage, particularly when the pumped fluid contains abrasives. All leaked fluids have to be contained and disposed of safely. If the fluid is also toxic, flammable, radioactive or environmentally damaging, the possibility of leaks, even minor ones, can be extremely dangerous. Leakages are one of the main causes of pump failures or shutdowns and the maintenance of seals and packing materials is expensive and time-consuming.
Environmental concerns and legislation has driven industry to implement cleaner pumping technology. A magnetic drive pump contains the pumped fluid completely within the pump housing. It only has a hermetic seal – a stationary gasket or O-ring – that is not subject to wear from moving parts and is therefore ideally suited to applications where no leakage can be tolerated either on safety grounds or because the costs of recovery and treatment are prohibitive.
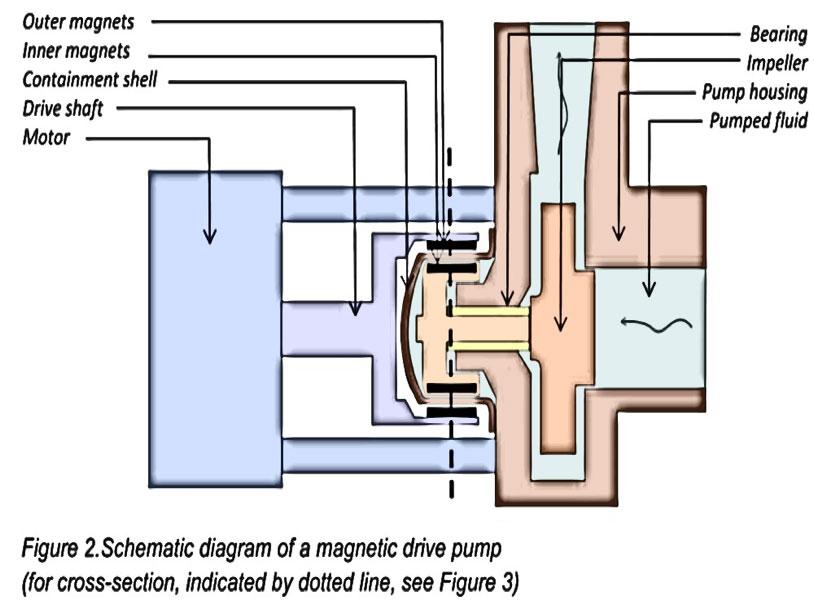
The coupled magnets are attached to two concentric rings on either side of the containment shell on the pump housing (Figures 2&3). The outer ring is attached to the motor’s drive shaft; the inner ring to the driven shaft of the impeller. Each ring contains about the same number of identical, matched and opposing magnets, arranged with alternating poles around each ring. The magnets are often made of rare earth metals such as samarium or neodymium alloyed with other metals. The most common combinations are Samarium-Cobalt and Neodymium-Iron-Boron. These complex alloys have two main advantages over traditional magnets:
